Understanding Blow Moulded Plastic Parts
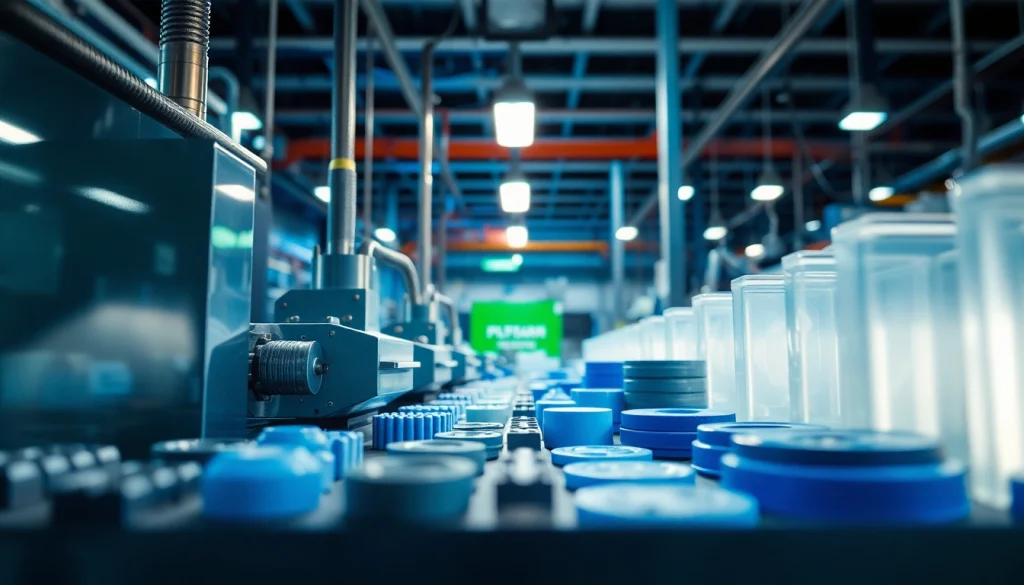
In the world of manufacturing, the pursuit of efficient and innovative methods for creating products is ongoing. One such method that has gained significant traction in various industries is blow moulding, particularly for the production of hollow plastic parts. Blow moulded plastic parts are widely utilized in multiple sectors, ranging from packaging to automotive components, due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility. In this article, we will delve deeper into what blow moulded parts are, explore the intricacies of the blow moulding process, and highlight their applications.
What Are Blow Moulded Plastic Parts?
Blow moulded plastic parts are created using a manufacturing process that converts plastic resin into hollow products. The blow moulding process involves heating a plastic tube until it becomes pliable and then inflating it with air inside a mold, allowing it to take the shape of the desired item. Typical products made through this method include bottles, containers, and various automotive parts.
The Blow Moulding Process Explained
The blow moulding process can be categorized into three primary types: extrusion blow moulding, injection blow moulding, and injection stretch blow moulding. Each type has distinct methodologies and applications:
- Extrusion Blow Moulding (EBM): In this process, a heated plastic parison is extruded through a die and then inflated into a cooled mold. It is ideal for producing large items like barrels or tanks.
- Injection Blow Moulding (IBM): Here, the process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create a preform, which is then placed in a blow mold and inflated. This method is well-suited for precision parts like bottles, where the tolerances must be tight.
- Injection Stretch Blow Moulding (ISBM): This hybrid process combines injection moulding for the preform with the blow moulding technique to stretch the preform and produce highly durable items, primarily PET bottles.
Common Applications of Blow Moulded Parts
Blow moulded plastic parts can be found across numerous industries, each leveraging the unique attributes of this manufacturing process:
- Packaging: The food and beverage industry often utilizes blow moulding for creating lightweight, durable bottles for liquids.
- Automotive: Automotive manufacturers employ blow moulded parts for fuel tanks, air ducts, and more due to their resilience and weight-saving properties.
- Consumer Goods: From toys to household products, the versatility of blow moulded parts enables the creation of a wide range of everyday items.
Materials Used in Blow Moulding
The choice of materials for blow moulding is vital in determining the functionality, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product. Understanding the various plastics and materials used in the process is essential for manufacturers and designers alike.
Types of Plastics for Blow Moulding
Several types of plastics are commonly used in blow moulding, each offering unique properties:
- Polyethylene (PE): Available in various densities (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE), polyethylene is known for its toughness and flexibility, making it a popular choice for bottles and containers.
- Polypropylene (PP): Recognized for its chemical resistance and stiffness, polypropylene is often utilized in automotive applications and container manufacturing.
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Widely used in beverage bottles, PET is lightweight and has good barrier properties that preserve product freshness.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC can be rigid or flexible, making it useful in various applications, including manufacturing pipes and fittings.
Benefits and Limitations of Various Materials
While the selection of materials offers various benefits, it’s crucial to consider their limitations as well:
- Benefits: Common advantages include lightweight characteristics, excellent moldability, and cost-efficiency, which often lead to reduced production costs and faster cycles.
- Limitations: Limitations may include susceptibility to UV degradation (in some plastics), lower impact resistance, and environmental concerns regarding recyclability.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Project
Selecting the correct resin is critical to ensuring that the final product meets design specifications and functional requirements. Factors to consider when choosing a resin include:
- End Use: Consider the environment in which the product will be utilized to determine the necessary strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
- Manufacturing Cost: Balance the material costs with the overall budget for production.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that selected materials meet safety and environmental regulations, especially for food and medical applications.
Advantages of Blow Moulded Plastic Parts
The advantages of blow moulded plastic parts make them an appealing choice for manufacturers across various industries. Understanding these benefits can provide significant insights into why this method is often preferred.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Blow moulded parts can be produced at a lower cost compared to other manufacturing methods such as injection moulding or rotational moulding. The reasons are:
- Lower tooling costs due to simpler molds.
- Faster cycle times, allowing for higher production rates.
- Reduced material waste through precise material usage.
Durability and Lightweight Characteristics
Another key advantage of blow moulded parts is their inherent strength and lightweight nature:
- Blow moulded parts typically have a thinner wall compared to similar injection-moulded parts.
- This feature not only reduces material use but also allows for easy handling and transportation.
Customization and Design Flexibility
The blow moulding process allows for significant design flexibility:
- Manufacturers can create complex shapes and sizes tailored to specific application needs.
- Options for integrating features such as handles, spouts, or threading directly into the design enhance product utility.
Challenges in Blow Moulding Manufacturing
Despite the numerous advantages, the blow moulding process is not without its challenges. Recognizing and addressing these issues is vital for successful manufacturing outcomes.
Overcoming Production Errors
Production errors can arise due to factors such as improper heating, mold misalignment, or pressure variations. To mitigate these issues:
- Establish detailed quality control protocols that monitor the entire blow moulding process.
- Invest in technology for automated adjustments to temperature and pressure.
Sustainability Concerns in Plastic Manufacturing
The environmental impact of blow moulding and the use of plastics is a growing concern. Strategies to enhance sustainability include:
- Utilizing recycled materials whenever possible, such as rPET (recycled PET).
- Designing products for recyclability and utilizing biodegradable alternatives where feasible.
Future Trends in Blow Moulding Technology
The blow moulding industry is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology leading the way:
- Integration of automation and artificial intelligence for improved efficiency.
- Increased use of eco-friendly materials to address environmental concerns.
- Emerging technologies like 3D printing potentially influencing blow moulding processes.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for Blow Moulded Parts
Selecting the right manufacturing partner is pivotal in ensuring the quality and efficiency of production. The right manufacturer can make a significant difference in the final product quality and the overall success of your project.
Key Factors to Evaluate Plastic Manufacturers
When considering manufacturers, the following factors should be evaluated:
- Experience and Specialization: Look for manufacturers who specialize in blow moulding and have a proven track record.
- Resource Availability: Assess their capabilities in terms of equipment, technology, and workforce.
- Quality Assurance: Investigate the quality control measures in place to ensure product consistency and reliability.
How to Assess Quality and Compliance Standards
It’s essential to ensure that a manufacturer adheres to recognized quality and compliance standards. This can be done by:
- Requesting documentation and certifications related to quality management systems, such as ISO certifications.
- Reviewing past case studies or product samples to assess their standard of work.
Questions to Ask Before Partnering
Before entering a partnership with a manufacturer, it is crucial to ask pertinent questions, such as:
- What are your lead times and production capabilities?
- Can you provide references or testimonials from previous clients?
- What is your approach to sustainable materials and processes?